Collaborating to achieve an eco-friendly Python !
Power consumption in ICTs is continually growing. Data centres currently account for 6% of global energy consumption and are a considerable drain on operators’ and service providers’ financial resources. Despite this, energy efficiency is still one of the factors most neglected by software developers.
Given this, Davidson and Inria are jointly conducting a research project on assessing and optimising the energy footprint of programming languages. The goal is to identify and establish a series of recommendations aimed at significantly reducing energy consumption for the long term. Due to its growing popularity, the research team is examining the opportunities provided by the Python language, its ambition being to reconcile performance, security and energy efficiency for a broad range of applications.
To reach this goal, the team has designed and rolled out a measurement tool based on PowerAPI . This software allows users to assess in real time the power the software uses by collecting metrics from the various hardware components (processors, memory, etc.) and the operating system.
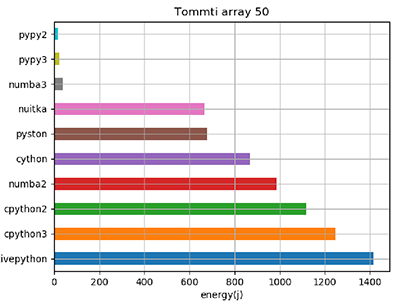
Using this measurement tool, the research team has compared the energy footprint of a variety of algorithms in different Python versions, and studied the impact of using specific libraries and variable classes over others.
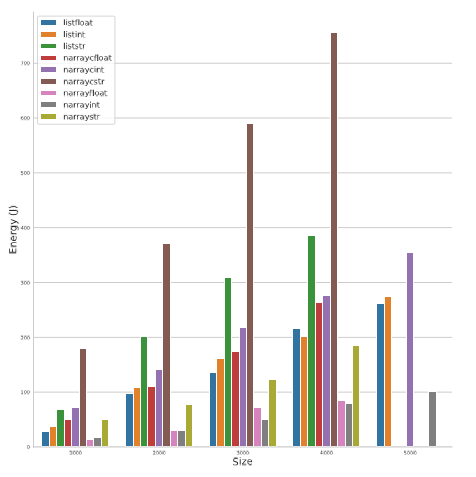
Moreover, a study was conducted on the impact of using a library and specific classes of variables compared with others.
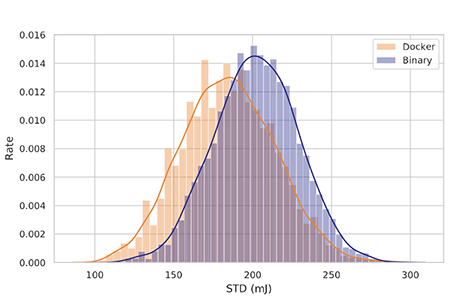
This data was used to characterise the contribution of each of the techniques and hardware components (based on the characteristics) to the overall energy footprint.
Following this work and drawing on the Python algorithms developed by Davidson’s IA-Twister team (automatic natural language processing, data collection and prediction, optimisation, text mining, etc.), the research team is planning to propose – for each class of algorithms – recommendations on the ideal compilation and execution environment, and the preferred libraries, as well as the coding conventions (order for executing conditions and loops), to give developers the most effective support in implementing more environmentally-friendly software.
To get more information on our R&D projects : innovation@davidson.fr

